Best Pressure Relief Chairs
Premium Pressure Relief Chairs for Enhanced Comfort and Care
Finding the perfect balance of support and relaxation is essential for long-term health. Our curated selection of Pressure Relief Chairs is designed to integrate seamlessly with your Living Room Furniture, providing specialised orthopaedic care without compromising on home aesthetics. Experience the ultimate in Australian comfort today.
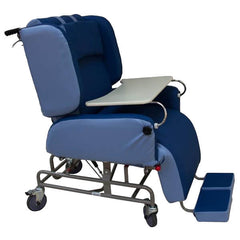
Alternating Air Pressure Relief Chair for Bariatric Patients
Advanced Seating Solutions for Pressure Management
Long periods of sitting can lead to discomfort and skin breakdown. Our range focuses on high-specification pressure redistributing materials that cater to high-risk users and those with limited mobility.
Key Features of Our Pressure Care Range
- High-Density Pressure Foam: Contours to the body to redistribute weight evenly across the seat.
- Breathable Medical-Grade Fabrics: Moisture-wicking materials to keep skin cool and dry.
- Ergonomic Postural Support: Contoured backrests and lumbar support to improve sitting posture.
- Adjustable Positioning: Motorised and manual tilt functions to shift pressure points throughout the day.
- Durable AU-Standard Construction: Built to withstand daily use in home and aged care environments.
Choosing the Right Chair for Your Needs
Whether you require a static orthopaedic chair for upright support or a fully motorised lift recliner for assistance with standing, our collection prioritises safety and ease of use for both the user and the carer.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do pressure relief chairs help prevent pressure sores?
These chairs use specialised foam and tilt-in-space technology to redistribute body weight away from bony prominences like the tailbone and hips.
Are these chairs suitable for high-risk patients?
Yes, many of our models feature multi-stretch fabrics and memory foam layers specifically designed for individuals at high risk of skin breakdown.
Can these chairs be used in aged care facilities?
Our pressure relief range meets strict Australian durability and safety standards, making them ideal for both private homes and clinical environments.
Do you offer delivery across Australia?
We provide reliable shipping for all our heavy-duty furniture to major cities and regional areas throughout Australia.